Japan is making significant strides to revitalize its semiconductor industry, with Rapidus—a consortium of eight Japanese companies—at the forefront of this initiative. Established in 2022, Rapidus aims to mass-produce 2-nanometer (nm) chips by 2027, positioning Japan alongside global leaders like TSMC and Intel in advanced semiconductor manufacturing.
Rapidus Chairman Tetsuro Higashi explained the current state of Japan's semiconductor industry at Semicon Japan 2022, stating,
“Japan has not only lost its semiconductor market share but also lacks cutting-edge logic semiconductor technology. Currently, Japan's semiconductor industry has not kept up with the global requirements for performance, cost, and speed. Rapidus aims to reclaim advanced logic semiconductor technology and establish a foundation for economic growth.”
Rapidus will focus on ultra-short TAT (Turnaround Time) design, supported by the Leading-edge Semiconductor Technology Center (LSTC), established jointly with national institutions to drive Rapidus’s development.
Higashi also explained the significance of developing 2nm chips: “To realize the industrial vision of future society, the United States, Taiwan, and South Korea are competing to develop ‘beyond 2nm’ technology. The industry believes that Japan currently has little demand for beyond 2nm chips, but this is a future industry that requires long-term development.”
Rapidus President and CEO Atsuyoshi Koike emphasized, “Speed is crucial for Rapidus. As product cycles shorten, collaboration between companies is key to reducing development time. Japan’s advanced logic semiconductors are 10 to 20 years behind. We are fortunate to have IBM providing GAA (Gate-All-Around) technology,” underscoring the importance of collaboration with IBM.
Current Developments:
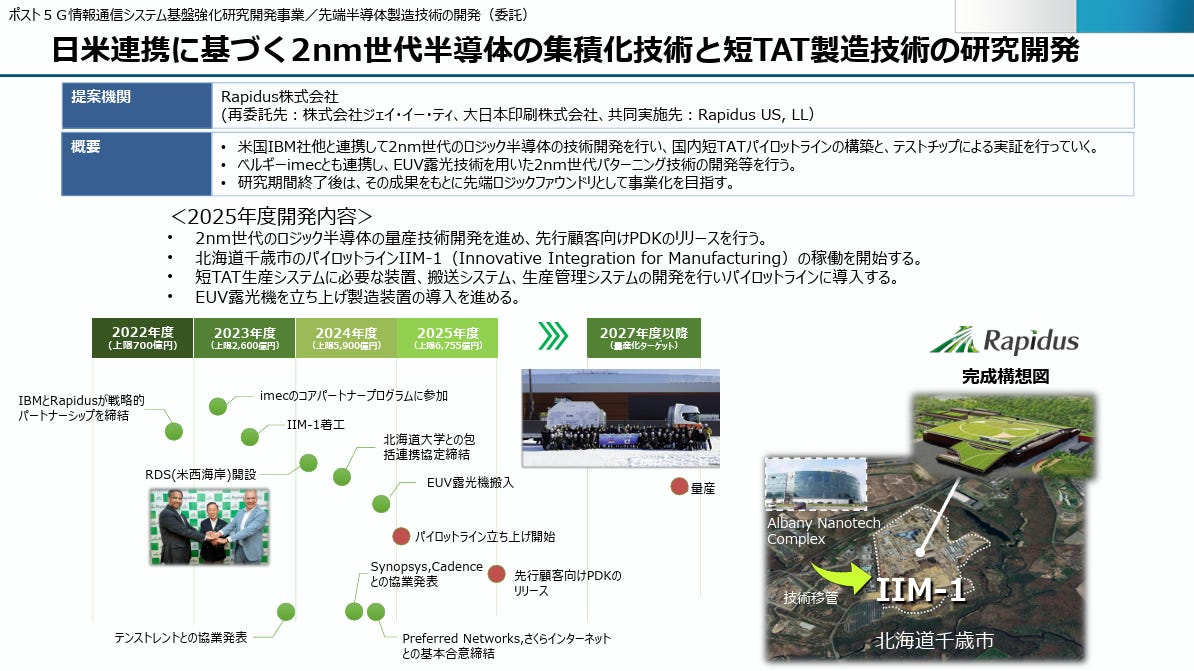
Rapidus was selected in November 2022 for the Next-Generation Semiconductor Research and Development Project under Post-5G Information Communication System Infrastructure Enhancement Research and Development Project. The allocated support for 2022, 2023, and 2024 totals 86.65 billion yen.
2024 Funding: 53.5 billion yen focused on advanced packaging technology for next-generation semiconductors.
2025 Funding (Plan): 67.55 billion yen (First half) + 12.7 billion yen (Second half).
Overall Budget Cap: 172.25 billion yen (Front-end: 54.2 billion yen, Back-end: 118.05 billion yen).
Breakdown by Year
2022: 70 billion yen - Establishment of basic technology development and research structure. Involvement of IMEC, IBM, Fraunhofer, etc.
2023: 26 billion yen - Expansion of the development framework, verification processes, and establishment of the Process Design Kit (PDK).
2024: 53.5 billion yen - Continued collaboration with IBM, Fraunhofer, STAR IME, and others for advanced packaging technology enhancement.
2025: 80.25 billion yen - Major focus on 2nm chip development, collaboration with Fraunhofer, IBM, and STAR IME.
2027: Goal to establish short TAT (Turnaround Time) production for 2nm semiconductors with advanced design kits and assembly methodologies.
Technological Partnerships: Rapidus has entered into strategic collaborations with industry leaders to bolster its technological capabilities. Notably, it partnered with IBM to develop 2nm-class process technology utilizing gate-all-around transistors. This alliance is expected to accelerate the development and commercialization of cutting-edge semiconductor technologies.
Infrastructure Expansion: The company is constructing a facility in Chitose City, Hokkaido, with plans to commence test production of 2nm chips in April 2025. This milestone is critical for validating their manufacturing processes and securing further investments.
Government Support: Recognizing the strategic importance of semiconductor self-reliance, the Japanese government has pledged substantial financial support. In November 2024, a $65 billion plan was unveiled to aid the domestic chip industry, with significant investments directed towards Rapidus and related initiatives.
Challenges Ahead:
Rapidus Completion Render Picture
Despite these advancements, Rapidus faces several challenges:
Talent Acquisition: There is a pressing need to cultivate a skilled workforce capable of driving innovation in semiconductor design and manufacturing. Initiatives like partnerships with educational institutions and training programs are underway to address this gap.
Global Competition: The semiconductor industry is highly competitive, with established players like TSMC, Intel, and Samsung investing heavily in advanced technologies. Rapidus must navigate this landscape by leveraging its unique strengths and fostering innovation.
Future Outlook:
Rapidus Corporation's collaboration with IBM, Fraunhofer, and A*STAR IME. The plan includes RDL interface board development, 3D packaging technology, mass production techniques, and assembly design kits. It outlines milestones for 2024–2025, aiming for comprehensive technological readiness and testing workflows for advanced 2nm chips.
Looking ahead, Japan’s semiconductor strategy involves a two-track approach:
Advanced Chip Production: Through Rapidus, Japan aims to produce cutting-edge 2nm chips, catering to high-performance applications and reducing reliance on foreign suppliers.
Legacy Chip Manufacturing: Collaborations with companies like TSMC focus on producing legacy chips (e.g., 22/28nm) to meet immediate industry needs without extensive capital investment.
These efforts reflect Japan’s commitment to re-establishing itself as a semiconductor powerhouse, ensuring technological sovereignty, and contributing to the global supply chain.
For Paid Members, SemiVision Research will discuss following topics:
Rapidus 2nm Customer Development Progress: Targeting AI and High-End Chip Markets
Comprehensive Government Support: Reclaiming Global Semiconductor Leadership
US-Japan Alliance: Technological Breakthroughs and Strategic Collaborations in 2nm Technology
2nm Chiplet and 3D Packaging: Rapidus’ Differentiation Strategy
Milestones and Strategic Timeline: 2024–2027 Roadmap
Challenges and Future Prospects for Japan’s Semiconductor Industry
Rapidus’ 2nm Journey and Japan’s Semiconductor Renaissance