TSMC’s Silicon Photonics Architecture: Why Couplers and Optical Engines Matter for the Future
Original Article by SemiVision Research (TSMC , Nvidia)
Driven by the demands of AI and high-performance computing (HPC), data center interconnects are reaching the limits of bandwidth, power efficiency, and latency. Silicon photonics has emerged as a key solution for next-generation optical interconnects, offering high speed, low power consumption, and seamless integration with advanced packaging. As a global leader in semiconductor manufacturing, TSMC is actively developing heterogeneous photonic-electronic integration architectures, with a particular focus on enhancing coupler design and process control—critical enablers for stable and efficient Optical Engines.
Through platforms such as COUPE, EPIC-BOE, and iOIS, TSMC is steadily building a comprehensive ecosystem to support Co-Packaged Optics (CPO) and high-bandwidth optical modules. Along this trajectory, NVIDIA is also on the verge of realizing its Photonic Interconnect vision, and TSMC’s robust silicon photonics modules and coupling structures are poised to play a foundational role in enabling this optical-electronic convergence.
At the 2025 IEEE ECTC, TSMC presented two significant papers on photonics. One was led by KC Hsu’s team, while the other was authored by Douglas’s team. The latter builds upon the foundational concepts of COUPE and extends previous work on iOIS and EPIC-BOE. This paper offers deeper insights and reinforces key architectural elements—making it highly relevant to NVIDIA’s Feynman AI chip and its Optical I/O strategy.
Notably, the paper highlights several critical aspects such as advanced coupler design and optical testing methodologies. Throughout the discussion, a central theme emerges: the future of Optical Engines lies in their seamless integration with advanced packaging platforms—a message that resonates strongly with ongoing industry trends.
Keywords: 2.5D CoWoS®, SoIC®, Co-Packaged Optics (CPO), Broadband Optical Engine (BOE), COUPE, COI, iFAU, silicon photonics, advanced couplers, vertical coupling, wafer-level process, optical waveguide, alignment accuracy, chip warpage tolerance.
At the 2025 IEEE ECTC, TSMC’s silicon photonics division published a new paper that further strengthens the COUPE concept. Led by TSMC Vice President K.C. Hsu, this work connects deeply with the themes addressed by ISIG and the TSMC * NVIDIA collaboration at Computex 2025. The SemiVision team will provide an in-depth analysis of this important contribution.
Broadband Optical Engine (BOE): TSMC’s Integrated Silicon Photonics Platform for Co-Packaged Optics
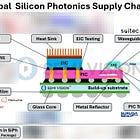
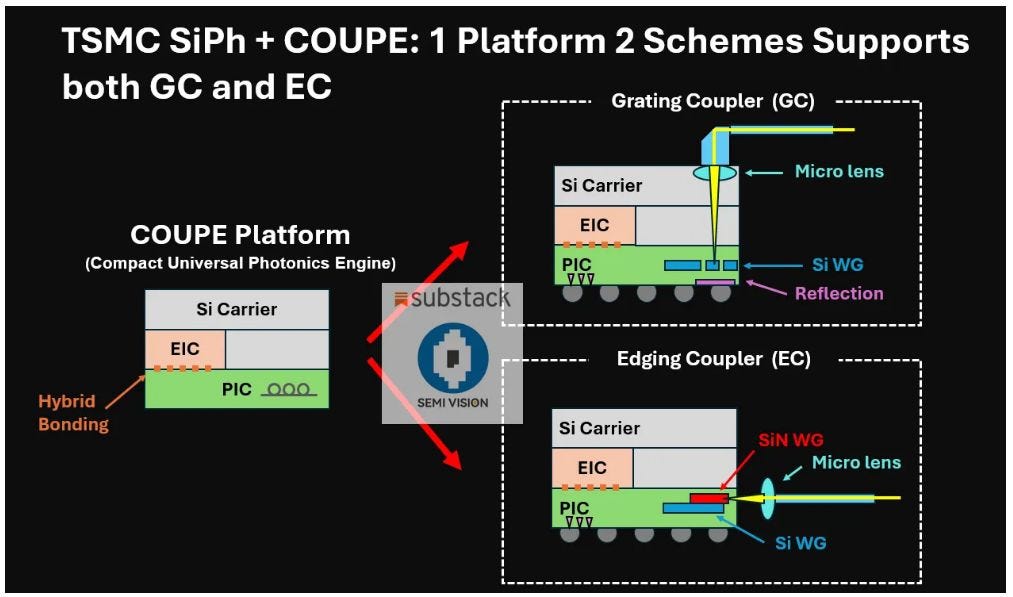
In response to the growing demands of bandwidth-intensive applications such as AI and high-performance computing, a new broadband optical engine (BOE) architecture has emerged, combining silicon photonics with advanced packaging technologies. This optical engine features the system-level integration of three key components—COUPE (Compact Universal Photonic Engine), COI (Complimentary Optical Interconnect), and iFAU (Integrated Fiber Array Unit)—to enable Co-Packaged Optics (CPO) within a 2.5D CoWoS® environment.
At the heart of this architecture lies COI, a critical component that facilitates low-loss optical signal routing. COI consists of paired optical couplers and precision-engineered structures that efficiently redirect light from the iFAU’s optical fibers into on-chip waveguides, guiding the signal toward the silicon photonics chiplet. This coupling pathway is essential for minimizing insertion loss and enabling high-performance optical-electrical co-integration.
One of the distinguishing features of the BOE system is its compatibility with wafer-level manufacturing. This process-oriented approach not only supports scalable bandwidth density—leveraging multi-wavelength operation and multi-row fiber arrays in the iFAU—but also ensures high manufacturability through inline process monitoring. By adopting a vertical optical coupling configuration, the system offers enhanced tolerance to chip warpage—a known challenge in advanced packaging. Unlike edge coupling (EC), which is highly sensitive to mechanical alignment, vertical coupling provides greater resilience and stability in real-world assembly conditions.
To validate the performance of this BOE platform, TSMC conducted a series of optical measurements across full 300 mm wafers. The results were then compared with simulation and modeling data to assess performance consistency and identify process sensitivities. The study revealed that discrepancies between modeled and measured optical performance are strongly influenced by several critical dimension (CD) parameters, including waveguide width, etch depth, sidewall profile, surface smoothness, and alignment precision.
These findings underscore the importance of rigorous process control in optical device fabrication. Even minor variations in structural dimensions or material properties can lead to measurable differences in optical loss and signal fidelity. As TSMC continues to scale its CPO capabilities through CoWoS® and SoIC® platforms, the integration of robust BOE technology will be instrumental in delivering next-generation bandwidth density and system-level efficiency.
Driven by the rising demands of AI and high-performance computing (HPC) for high-speed and low-latency data transmission, silicon photonics is rapidly emerging as a core technology for next-generation optical interconnect solutions. To address the growing need for greater bandwidth density and energy efficiency in data centers and accelerator platforms, this study introduces a novel Broadband Optical Engine (BOE). The BOE integrates advanced packaging technologies with silicon photonic modules to enable Co-Packaged Optics (CPO) architectures, offering a scalable and efficient path forward for optical I/O in AI-driven infrastructures.
For Paid Members, SemiVision will discuss topics on
COUPE (Compact Universal Photonic Engine): Design Principles and Technology Positioning
COUPE: Deep Compatibility with Advanced Process Platforms
COUPE: High Scalability and Platform Flexibility
COUPE: Support for Diverse Integration Scenarios:
TSMC COUPE : Industrial Implications and Future Outlook
TSMC Develop New Photonic Era : From Single-Channel Coupling to Wafer-Scale Multi-Channel Modularization
Silicon Photonics Broadband Optical Engine (BOE): A Comprehensive Overview from System Architecture to Process Control
Five-Stage Optical Coupling Architecture in BOE (Broadband Optical Engine)
TSMC’s In-House Optical Test Platform for Silicon Photonics Modules
TSMC Demonstrates 40-Channel iFAU-to-COI Coupling with High Efficiency and Consistency
TSMC Demonstrates Ultra-Low-Loss COI Transmitter Coupler in O-Band
TSMC Demonstrates Free-Space Optical Coupling Loss Between COI and COUPE in BOE
TSMC Leverages Machine Learning to Analyze Coupling Loss and Process Parameters in BOE
COUPE (Compact Universal Photonic Engine) Rx Module: Coupling Loss Statistics for Vertical-to-Horizontal Waveguide Transition
Weighted Impact Analysis of Process Parameters on Coupling Loss in the COUPE Rx Coupler
Coupling Loss Analysis in the Final Waveguide Segment of the BOE (Broadband Optical Engine)
Summary to TSMC COUPE Platform